doi: 10.56294/nds2024106
ReviEW
Technology and conscious eating: a necessary convergence
Tecnología y alimentación consciente: una convergencia necesaria
María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo1
1Universidad Siglo 21, Ingeniería en software. Córdoba, Argentina.
Cite as: Rabozzi Orelo MJ. Technology and conscious eating: a necessary convergence. Nursing Depths Series. 2024; 3:106. https://doi.org/10.56294/nds2024106
Submitted: 20-06-2023 Revised: 18-09-2023 Accepted: 01-01-2024 Published: 02-01-2024
Editor: Dra.
Mileydis Cruz Quevedo ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: in recent years, society presented a growing interest in leading a healthy life, which boosted the development of technological tools focused on a balanced diet. In this context, conscious eating has positioned itself as an essential practice. Andrea A. Fernández defined it as the act of paying full attention to the moment of eating, moving away from strict diets and promoting sustainable habits. The Universidad Valle del Grijalva reinforced this vision by understanding the eating plan as a comprehensive, personalized approach oriented to lasting wellness.
Development: to support these habits, the development of mobile applications using modern technologies was proposed. SwiftUI, Apple’s framework, facilitated the creation of declarative and efficient interfaces. The MVVM architecture made it possible to better organize the code by separating the logic from the user interface, improving scalability. On the backend, Node.js enabled efficient handling of multiple simultaneous requests, while MongoDB offered flexibility in storing large volumes of unstructured data. In addition, analysis of existing applications revealed that many offered useful features such as product scanning or habit monitoring, but few managed to truly integrate a conscious, personalized approach.
Conclusions: the analysis demonstrated that it was possible to unite advanced technology and mindful nutrition in an innovative solution. Opportunities were identified to design an application that would not only function as a monitoring tool, but also educate and motivate the user to adopt healthy habits, based on mindfulness and effective personalization.
Keywords: Conscious Feeding; Technology; Customization; SwiftUI; MongoDB; MongoDB.
RESUMEN
Introducción: en los últimos años, la sociedad presentó un creciente interés por llevar una vida saludable, lo cual impulsó el desarrollo de herramientas tecnológicas enfocadas en una alimentación equilibrada. En este contexto, la alimentación consciente se posicionó como una práctica esencial. Andrea A. Fernández la definió como el acto de prestar atención plena al momento de comer, alejándose de las dietas estrictas y promoviendo hábitos sostenibles. La Universidad Valle del Grijalva reforzó esta visión al entender el plan alimenticio como un enfoque integral, personalizado y orientado al bienestar duradero.
Desarrollo: para apoyar estos hábitos, se propuso el desarrollo de aplicaciones móviles mediante tecnologías modernas. SwiftUI, el framework de Apple, facilitó la creación de interfaces declarativas y eficientes. La arquitectura MVVM permitió organizar mejor el código al separar la lógica de la interfaz de usuario, mejorando la escalabilidad. En el backend, Node.js posibilitó el manejo eficiente de múltiples solicitudes simultáneas, mientras que MongoDB ofreció flexibilidad en el almacenamiento de grandes volúmenes de datos no estructurados. Además, el análisis de aplicaciones existentes reveló que muchas ofrecieron funciones útiles como el escaneo de productos o el monitoreo de hábitos, pero pocas lograron integrar verdaderamente un enfoque consciente y personalizado.
Conclusiones: el análisis demostró que era posible unir tecnología avanzada y nutrición consciente en una solución innovadora. Se identificaron oportunidades para diseñar una aplicación que no solo funcionara como herramienta de seguimiento, sino que también educara y motivara al usuario a adoptar hábitos saludables, basados en atención plena y personalización efectiva.
Palabras clave: Alimentación Consciente; Tecnología; Personalización; SwiftUI; MongoDB.
INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, the concern for leading a healthy life has driven the interest in technological tools that promote balanced and personalized eating. In this context, mindful eating emerges as a key practice, since it implies paying full attention to the act of eating, as pointed out by Fernández(1), who defines it as the act of devoting full attention to the moment of eating. This perspective moves away from strict or temporary diets and promotes sustainable habits adapted to individual needs. This is reinforced by the Universidad Valle del Grijalva(2), which understands the dietary plan as a comprehensive and personalized approach that seeks positive and sustainable results over time, promoting a healthy life.
To support this type of practices, the development of nutrition-oriented mobile applications becomes a powerful tool. The use of modern technologies such as SwiftUI, MVVM, Node.js and MongoDB allows creating more efficient, interactive and adaptable solutions to users’ needs. SwiftUI, Apple’s framework, facilitates the creation of modern and declarative user interfaces, simplifying the development process and offering a more fluid experience. The MVVM architecture allows a clear separation of business logic and interface, improving scalability and code maintenance.
On the backend, technologies such as Node.js and MongoDB complement the application structure. Node.js, with its ability to handle multiple simultaneous requests, allows building highly efficient applications suitable for dynamic environments. MongoDB, being a document-oriented NoSQL database, offers great flexibility to adapt to the constant changes that can occur in a custom nutrition application, in addition to handling large volumes of unstructured data.
In addition, the competitive analysis shows a current overview of the existing applications on the market related to dietary planning. Each one offers particular features, from product scanning to food habits tracking, demonstrating the growing interest in technological solutions that help improve people’s quality of life. This assessment allows us to identify opportunities for improvement and underserved niches, serving as a basis for the design of an application that combines conscious eating, advanced technology and effective personalization.
DEVELOPMENT
Problem Domain
To analyze the problem domain, it is important to reflect on conscious eating and on the meaning of meal plan and its difference with strict diets. Fernández(1) expresses that “conscious eating consists of devoting full attention to eating”. At the same time, The University of Valle del Grijalva(2) describes: “A plan is an integral element, adapted to personal characteristics, that aims at beneficial and sustainable results, oriented to develop eating regimens to live healthily in general.”
ICT (information and communication technology)
SwiftUI
Apple’s modern framework for developing user interfaces in iOS declaratively. It facilitates the creation of applications by allowing the appearance and behavior of interfaces to be defined in a simple way, reducing code complexity and improving the development experience.
MVVM
The MVVM architecture in SwiftUI is used to separate business logic from the user interface, which promotes more modular and maintainable code. This allows developers to better manage UI updates and application state, providing a clear structure for robust and scalable application development.(3)
Node.js
JavaScript-based open source platform designed for building efficient and scalable backend applications. It allows developers to handle multiple requests simultaneously and is ideal for modern Internet-connected applications, such as those that integrate artificial intelligence and augmented reality services.
MongoDB
Document-oriented NoSQL database management system that stores data in a JSON-like format. It offers high flexibility and scalability, allowing it to handle large volumes of unstructured data efficiently. It is ideal for applications that need to adapt to rapid changes in data schemas and seek horizontal scalability.(4)
Competition
The following is a comparative analysis of some existing applications on the market that focus on food planning. Each of these applications offers different functionalities, from food scanning to food habit monitoring, but differ in the way they address these needs.(5,6) The analysis seeks to highlight the main features of each app and their specific approach to helping users improve their eating.
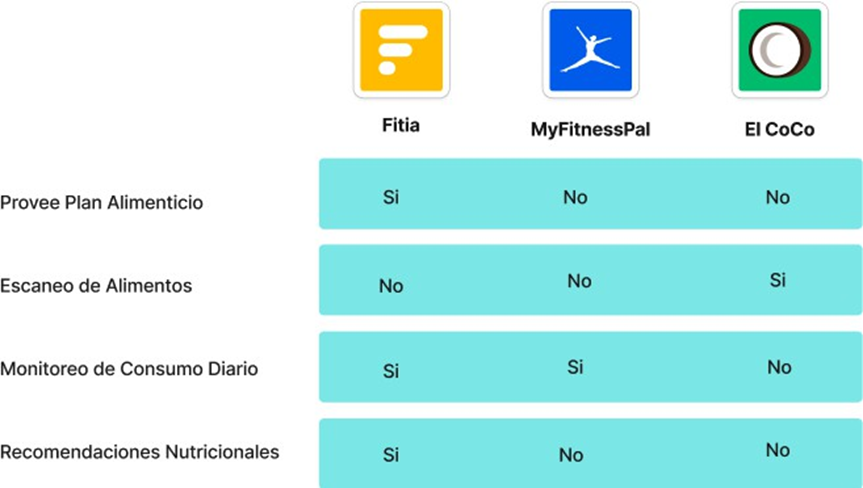
Figure 1. System competencies
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, the present analysis evidences the relevance of integrating technology with the promotion of healthy eating habits, through the development of mobile applications focused on conscious eating. This practice, understood as mindfulness when eating, moves away from traditional restrictive diets and is oriented towards the creation of personalized, sustainable eating plans tailored to individual needs. Such an approach not only encourages a better relationship with food, but also promotes overall long-term wellness.
The incorporation of modern technologies such as SwiftUI, MVVM, Node.js and MongoDB proves to be fundamental to the design of innovative digital solutions in the field of nutrition. SwiftUI enables a more efficient and visually appealing creation of interfaces, while MVVM architecture ensures a clear and maintainable structure in software development. On the backend, Node.js brings efficiency and performance in the face of multiple simultaneous requests, making it ideal for dynamic applications. MongoDB, on the other hand, offers flexibility in the management of unstructured data, which is essential in platforms that require constant adaptation to user preferences and characteristics.
In addition, the problem domain analysis highlights the importance of understanding the difference between conscious eating and conventional diets. Through sources such as Andrea A. Fernández and the Grijalva Valley University, the idea that a dietary plan should be comprehensive, personalized and focused on sustainable wellness is reinforced, which consolidates the need for technological tools that support this paradigm.
The study of the current competition allows us to identify gaps and opportunities in the market, such as the lack of an application that effectively combines advanced technology with a genuinely conscious and personalized approach to nutrition. This opens the possibility of developing an innovative solution that not only functions as a nutritional assistant, but also educates and motivates the user to adopt healthier habits from a holistic perspective.
In short, this project proposes a convergence between health, technology and personalization, demonstrating that it is possible to take advantage of the capabilities of information technology to positively impact people’s quality of life. Thus, the foundations are laid for the development of an application that responds to the real needs of users on their way to a more conscious and balanced diet.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES
1. Fernández AA. Alimentación consciente: principios y prácticas. Revista de Nutrición Integral. 2022.
2. Universidad Valle del Grijalva. Universidad Valle del Grijalva; s.f. Disponible en: https://www.uvg.edu.mx
3. SwiftBeta. SwiftBeta; 2023. Disponible en: https://www.swiftbeta.com
4. MongoDB. MongoDB Pricing. MongoDB Inc.; s.f. Disponible en: https://www.mongodb.com/pricing
5. Comisión Honoraria para la Salud Cardiovascular. Comisión Honoraria para la Salud Cardiovascular; s.f. Disponible en: https://www.cardio.com.uy
6. MyFitnessPal. MyFitnessPal; s.f. Disponible en: https://www.myfitnesspal.com
FINANCING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION:
Conceptualization: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Data curation: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Formal analysis: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Research: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Methodology: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Project Management: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Resources: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Software: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Supervision: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Validation: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Visualization: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Writing - original draft: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.
Writing - proofreading and editing: María Julieta Rabozzi Orelo.